Sanitary napkins, commonly referred to as pads, are essential products in women’s personal hygiene, playing a crucial role in managing menstrual flow. Over the years, the materials used in the manufacturing of sanitary napkins have undergone significant transformations, ensuring better comfort, effectiveness, and environmental sustainability.
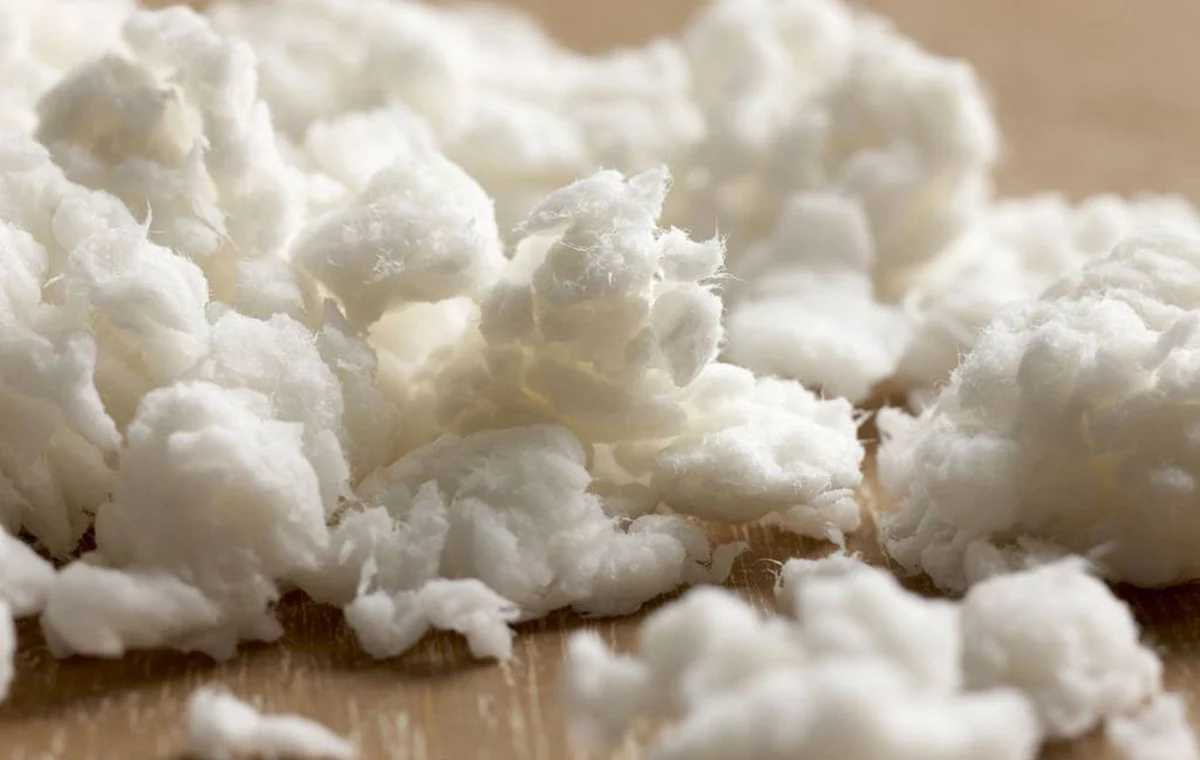
Early Materials and Their Limitations Historically, sanitary napkins were made from simple materials such as cotton, wool, and linen. While these materials were relatively absorbent, they posed several issues. Traditional cotton or linen pads were often bulky, less effective at moisture control, and inconvenient for use during physical activities. Additionally, the lack of standardized production methods meant considerable variability in quality and efficacy, leading to discomfort and even health issues for users.
Introduction of Synthetic Fibers With advancements in textile technology, the late 20th century saw the introduction of synthetic materials like polypropylene and polyethylene. These materials provided several advantages over natural fibers. For instance, synthetic fibers are lighter, thinner, and can be engineered to enhance absorbency and moisture-wicking capabilities. The softly textured surfaces made from these materials improved comfort, while their design allowed for a more discreet fit under clothing.
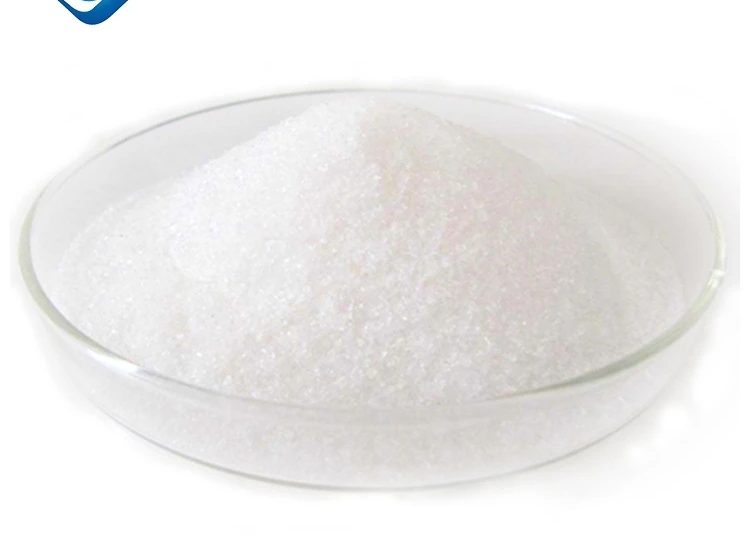
Innovations in Absorbent Core Materials The heart of any sanitary napkin is its absorbent core. Initially, cellulose-based materials were commonly used, but they absorbed moisture more slowly and often led to leakage. The introduction of superabsorbent polymers (SAP), such as sodium polyacrylate, has revolutionized the industry. SAP can absorb many times their weight in liquid, allowing for thinner pads with greater absorption capacities. This innovation has enabled manufacturers to create ultra-thin products without sacrificing performance.
Enhanced Breathability and Comfort In response to consumer demands for greater comfort and health-conscious products, manufacturers have developed breathable materials and designs. The use of non-woven fabrics and microporous films has increased airflow, reducing moisture buildup and the risk of irritation or infections. Additionally, pads now often feature anatomical designs and flexible materials that move with the body, enhancing wearability during various activities, including sports.
Biodegradable and Sustainable Options As environmental awareness has grown, the sanitary napkin industry has begun to shift towards more sustainable practices. Traditional products can take hundreds of years to decompose, leading to increased waste in landfills. In recent years, manufacturers have started exploring biodegradable materials made from organic cotton, bamboo fibers, and other renewable resources. These innovations not only help reduce the ecological footprint but also appeal to consumers seeking eco-friendly alternatives.
Future Trends in Sanitary Napkin Materials Looking ahead, the focus on women’s health, sustainability, and technological integration will continue to shape the evolution of sanitary napkin materials. Research into innovative materials that combine absorbency, biodegradability, and comfort is ongoing. Additionally, smart technologies embedded in sanitary products, such as moisture sensors that indicate when a change is needed, could enhance user experience and promote better hygiene practices.
Conclusion The development of materials in sanitary napkins reflects broader trends in health, comfort, and environmental sustainability. From early bulky fabric pads to today’s ultra-thin, highly absorbent, and eco-friendly options, the industry has continually innovated to meet the needs of users. As technology and materials science advance, we can expect even more improvements in the safety, comfort, and ecological impact of sanitary products, paving the way for a healthier and more sustainable future for women worldwide.